Harmonic Gearbox Slides
What is it?
- A type of gear system whose main advantage (for our purpose) is that it has no backlash
- Also allows for high gear reduction ratios, torque, and accuracy
- Another common name is Strain Wave Gearing
- (Harmonic Drive is a brand name for a company’s strain wave gear)
Backlash
- Regular types of toothed gears have small gaps between the teeth of mating gears
- This allows them to mesh and rotate smoothly and without damage
- A downside of this is it lets the gears “wiggle” a little bit - the small gap means that the gears can move back and forth a small amount without moving the motor
How does it work?
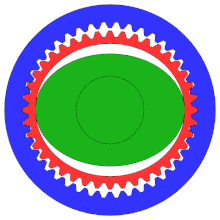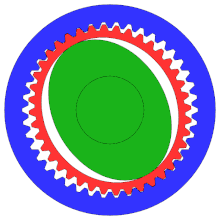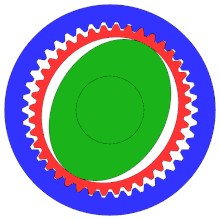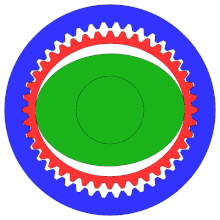
Main parts
- Wave generator (green)
- Elliptical shaped
- Centre“hub” where the input shaft attaches, and a special bearing on the outside
- Flex spline (red)
- Cup made of flexible metal material
- External teeth on the open end of the cup
- End of the cup can change shape but the base is rigid
- Output attached to the bottom of the cup
- Circular spline (blue)
- Rigid ring with inner teeth
- Two more teeth than the flex spline
- This is what allows the flex spline to rotate
- Output ring
- Can have a fourth part depending on the harmonic drive (as explained in this video)
- located directly below the blue circular spline/stator ring. It has two teeth less than the circular spline (but the same circumference)
- The flex spline acts to “line up” the two teeth on either end of the wave generator (using the wedge force of the flex spline teeth on both the output ring and circular spline) causing the output ring to slowly turn
Functionality
- Wave generator inserted in the flex spline, causes the flex spline to assume the elliptical shape
- As the wave generator rotates, the flex spline is deformed around it
- Only the teeth at the ends of the elliptical flex spline mesh with the teeth in the circular spline
- Because of the tooth count difference, the flex spline rotates in the opposite direction by two teeth per wave generator rotation
- How does it have no backlash: the fixed shape of the elliptical generator means that there is always pressure along the major axis between the flex spline and the circular spline. This results in the flex spline being unable to wiggle, the flex spline connects to the output gear leading to no backlash
Examples of the flex spline’s rotation
More Technicalities
Calculating gear ratio
The gear ratio is calculated differently depending on the driving arrangement. The standard
arrangement has the circular spline fixed, the wave generator as the input, and the flexspline as the output. In this case, the gear ratio is -input speedoutput speed. Other examples are shown on page 17 here. Products from Harmonic Drive®️, are displayed using this gear ratio.
Styles
Cup
- Flexspline is a cup that fits through the circular spline
- Circular spline is the largest diameter
- Wires exterior
Hat
- Flexspline is shaped like a top hat (like cup style, but with a “brim” on the output)
- Brim of the flexspline is the outermost diameter
- Hole for wires through the middle
Where we need it
Location | Voltage (V) | Max Current Draw [A] | Stall Torque (N-m) | Max Speed (RPM) | Reduction Ratio To Encoder | Max Speed at Encoder (RPM) | Datasheet |
Elbow | 12 | 25 | 0.669 | 4150 | 252 | 16.46825397 | |
Wrist | 24 | 5.5 | 4.8 | 67 | 1 | 67 |
Elbow
- Biggest issue
Wrist
- Second priority
- Would require significant design change
Advantages and disadvantages
Advantages
Advantage | Details | Significance |
Lightweight | ||
Precise | The robot’s claw has to perform careful tasks so high precision is very important | |
They require little maintenance -they are either working or broken and need replacing -apparently very reliable | -would not require maintenance (as much) -lasts a long time (fewer long term costs and time associated) | |
Preloaded | Def: applying pressure to fix a component in place/applying extra pressure to ensure the component can handle future strain -helps to ensure zero backlash for life of gear -top of flex spline is circular (output side) while the bottom is elliptical therefore flex spline teeth flare out slightly -this results in a conical angle that helps to preload the flex spline and circular spline -preloading removes free internal clearances (no shifting) | |
repeatability | -maintains positional accuracy when repeating a task over and over and over again |
Disadvantages
Disadvantage | Details | Significance |
EXPENSIVE | - None of the principle suppliers have prices listed (that I could find) but other sources show the price to be several hundred dollars for one unit - Would likely need to get sponsored in order to actually acquire these | |
Low speed output | - The high gear ratio means that the output speed is significantly lower than the input speed - This could be more or less important depending on the joint it’s used on |
Suppliers
Harmonic Drive ®️
- One of the original companies to commercialize strain wave gearing
- This is probably the most reliable source, they also have the most variety and documentation
- Doesn’t sponsor (according to Lance) :( not surprising
Cone Drive
Details:
- Production centres in the US
- Large variety of options
Product options:
- Offers component sets (just the plain module, would require custom housing) and gearheads (component set with housing, easier to attach to things)
- Cup, hat, or ring style
- Ring: axially compact and hollow center but has backlash
- Only offers gearheads for cup or hat
GAM
Details:
- American company
- Very positive values - maybe open to sponsorship?
Product options:
- Offers component sets and gearheads (I think)
- Cup or hat style with different options for input shafts
- Includes an “ultra thin” option
Kofon
Details:
- Chinese company
- Not too many options but probably enough to suit our needs
Product options:
- Component set (closed center)
- A few different gearhead styles (hollow or closed center)
[still to research]
Make our own
- Probably not the best accuracy which completely defeats the purpose
- Cheap though!
Usage examples
From Cone Drive website
From Harmonic Drive®️ website
From this video (technically a cycloid gearbox, not harmonic drive, but similar enough concept)
From here
General design observations
- Styles: I’ve been working off of the examples in this section but there are others if you look at the suppliers section. The cup and hat seem like the most common and useful options which is why I was focusing on them. Don’t forget there are options with hollow centres (although less)
- Elbow: The majority of real world examples have each segment offset from the previous one, with (I assume) the gearbox in one segment and the motor sitting inside the other. However I don’t think that will work for us because the bicep is much less heavy duty than those examples and is not designed to hold the entire weight of the forearm on one side. It probably wouldn’t hold and if it did it would unbalance the arm a lot.
- Elbow: Keep the width of the forearm in mind, because that can’t change unless we decide to replace the wrist gearbox (or unless you really want to get into redesigning the wrist)
- Wrist: This is lower priority but if we decide to go this route it could give us more freedom with the elbow. However it would require a significant design change
Other important info
- Cycloidal drive could be an alternative?
Next Steps
- Research more options for sponsors
- Figure out specs/styles for specific products we would need
- Lightning talk on everything above for the rest of the team
- CAD ideas for integration into robot
- Contact potential sponsors (hopefully with CAD to show)
Links
Information
Strain wave gear - Zero Backlash Gearhead | Harmonic Drive
Technical info (Harmonic Drive company)
Pictures
Harmonic Drive®️ robotics example