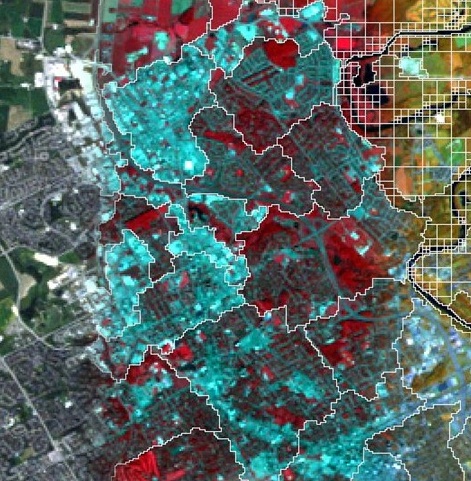
Remote sensing
Remote sensing involves the acquisition of information about a surface, object, or other phenomenon from devices that are not in contact with the feature under investigation. This is performed by active or passive sensors. An active sensor supplies its own source of energy (e.g., LiDAR or radar), whereas a passive sensor measures electromagnetic radiation reflected or emitted by an object (e.g. Landsat, Sentinel 2).
If you need assistance for a remote sensing project in terms of data processing or data acquisition, please contact Mike Lackner.
Software
All Windows teaching computer labs in Environment have the following software installed:
- ENVI/IDL: Comprehensive remote sensing software.
- PCI Catalyst (former Geomatica): Comprehensive remote sensing software.
- QT Reader: Freely available LiDAR point cloud viewer.
- SNAP: Free open-source remote sensing software, developed by the European Space Agency (ESA), specialized for radar applications.
The links above to the vendors' websites include gateways to useful help pages and tutorials about the respective software packages.
There are other remote sensing software that might be of interest. A few examples are provided below:
- LASTOOLS: Free open-source LiDAR processing software, requires no installation and thus can be downloaded and used in our labs.
- Google Earth Engine: Cloud-based image processing platform that is free for research, education, and non-profit use.
Data resources
The Geospatial Centre located in the Dana Porter Library holds an image archive that includes air photos and satellite imagery.
Mike Lackner in ETIS can also assist you with finding data for remote sensing projects based on individual needs.
Related content
If you have technical issues, Please submit a request to the ETIS Jira Queue. If you need help after hours or on the weekends, contact IST Service Desk.