Parallel Circuits
Table of Contents
What are Parallel Circuits?
Parallel circuits are circuits in which all electrical components are only connected using parallel connections [1]. A parallel connection occurs when electrical components are connected across each other's leads [2]. Thus, every electrical component in a parallel circuit is directly connected across every other electrical component in the circuit. In addition, every electrical component in a parallel circuit will have the same voltage across it [3].
What are the three principles of Parallel Circuits?
- Voltage:Voltage is equal across all components in a parallel circuit.
- Current: The total circuit current is equal to the sum of the individual branch currents.
- Resistance: Individual resistances diminishto equal a smaller total resistance rather than add to make the total.[4]
The equation for resistance in parallel circuits:
The equation for capacitors in parallel circuits:
A parallel capacitor circuit is an electronic circuit in which all the capacitors are connected side by side in different paths so that the same charge or current will not flow through each capacitor. When a voltage is applied to the parallel circuit, each capacitor will get the different charge.
The way to calculate total Capacitance in a parallel circuit is the same as to calculate total resistance in a series circuit.
The equation for inductors in parallel circuits:
When inductors are connected in parallel, the total inductance is less than any one of the parallel inductors' inductances. Again, remember that the definitive measure of inductance is the amount of voltage dropped across an inductor for a given rate of current change through it.
The way to calculate total Inductance in a parallel circuit is the same as to calculate total resistance in a parallel circuit.
Measuring
To measure current, you must insert the ammeter into the circuit to intercept the electric charge flowing in the wires. That means you must "break the circuit" by lifting a lead, and then complete the circuit using the probes of the ammeter.
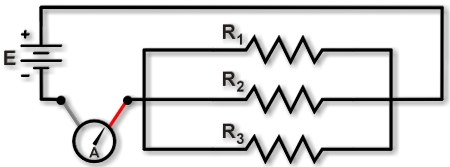
To measure a circuit's total current, lift a lead connected to the battery (or power source) and insert the ammeter, as shown in Figure 1. On a breadboard, this requires lifting the lead that provides power to the parallel resistors. The ammeter then measures the sum of the current through all the parallel resistors.
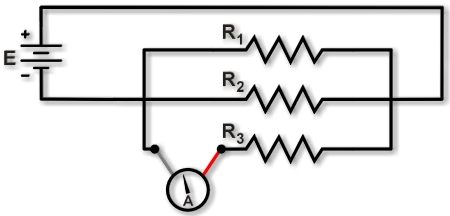
To measure the current through just one resistor, lift one resistor's lead and insert the ammeter, as shown in Figure 2. On a breadboard, this requires lifting the lead of one resistor and connecting the ammeter probes between the lifted lead and the power source. The ammeter then measures the current through a single resistor.
Measuring current for whole circuit.
Measuring current through resistor R3. [6]
Measure voltage without isolating the components. Voltage is the easiest thing to measure with a multimeter. To measure resistance of a component, you must turn off the power and take the component out of the circuit. To measure a current you must put the meter in the circuit, which means cutting a wire to insert the meter. Measuring voltage is as easy as placing the meter probes at two points and reading the meter that indicates the voltage difference between the two points. [7]
References
[1] “Physics Tutorial: Parallel Circuits,” The Physics Classroom. [Online]. Available: https://www.physicsclassroom.com/class/circuits/Lesson-4/Parallel-Circuits. [Accessed: 22-Jan-2021].
[2] “What are ‘Series’ and ‘Parallel’ Circuits?: Series And Parallel Circuits: Electronics Textbook,” All About Circuits. [Online]. Available: https://www.allaboutcircuits.com/textbook/direct-current/chpt-5/what-are-series-and-parallel-circuits/. [Accessed: 22-Jan-2021].
[3] “Parallel Circuits - Circuits Video Lecture,” All About Circuits. [Online]. Available: https://www.allaboutcircuits.com/video-lectures/parallel-circuits/. [Accessed: 22-Jan-2021].
[4] "Simple Parallel Circuits, Chapter5 - Series And Parallel Circuits," Vol 1 Direct Circuit. [Online]. Available:https://www.allaboutcircuits.com/textbook/direct-current/chpt-5/simple-parallel-circuits/. [Accessed: 17-Jun-2021]
[5] "Alternating Current versus Direct Current," Physics, Electric current. [Online]. Available:https://courses.lumenlearning.com/physics/chapter/20-5-alternating-current-versus-direct-current/. [Accessed: 23-Jun-2021].
[6] "Sparks Tutorial",[Online]. Available:http://sparks-activities.concord.org/sparks-content/tutorials/tutorial-10.html.[Accessed: 28-Jun-2021].
[7] "How to Find Voltage & Current Across a Circuit in Series & in Parallel," Electricity and Magnetism: What Are They & Why Are They Important?[Online]. Available:https://sciencing.com/voltage-across-circuit-series-parallel-8549523.html.[Accessed: 23-Jun-2021].
Contributors:
| User | Last Update |
|---|---|
| Mayurakhi Khan | 1233 days ago |
| - Lazo | |
| Former user (Deleted) | |
| Former user (Deleted) | |
| Former user (Deleted) | |
| Former user (Deleted) | |
| Former user (Deleted) |