Table of Contents
What is Sensor Interfacing?
- Interfacing enables a system to read out information from an input signal that is generated by a sensor and then providing an output signal that is easy for the host system to display and process
- Interfacing of sensors usually involves a mix of amplification, filtering and other signal conditioning in order to produce an output signal that the computer would be able to process
- There are two main signals that are used: Analog and Digital
Analog
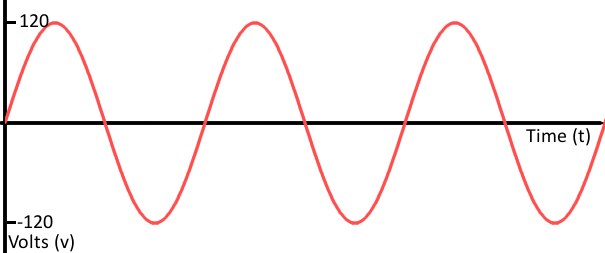
Analog Signal
- An analog signal is a continuous signal in which one time-varying quantity (such as voltage, pressure, etc.) represents another time-based variable.
- An analog system allows for a theoretically infinite number of values to be represented
- Video and audio transmissions are often transferred or recorded using analog signals.
- Pure audio signals are also analog.
- The signal that comes out of a microphone is full of analog frequencies and harmonics
Analog Electronics
- Most electronic components are analog (Ex: resistors, capacitors, inductors and diodes)
- Circuits built with a combination of the components are usually analog
- Analog sensors can be complex designs which include many components or they can be vey simple
| Analog Signal Graph |
Digital
Digital Signal
Digital signals must have a finite set of possible values
The set of values can be between two and a large number that is not infinity
Most commonly, the values will be one of the two values
For example, it can be 0V or 5V
Or the digital signal can be discrete representation of an analog waveform
From far away it looks like the line is smooth and analog but when zoomed in there are small discrete steps as the signal tries to approximate the value
Examples of digital signals are HDMI for video (the audio), MIDI, I2S, or AC'97 for the audio
| Digital Signal Changes between two Values | When Digital Signal Represents an Analog Waveform |
Digital Electronics
Digital circuits operate by using digital, discrete signals
These systems are usually made of a combination of transistors, logics gates and at higher levels, microcontrollers, and other computing chips
Most processors whether they are big and found in a computer or tiny microcontroller, they usually operate in the digital realm
Digital circuits usually used binary scheme for digital signaling
These systems assign two different voltages as different logic levels
A high value usually 5V, 3.3V, or 1.8V represent one values
The other low value is usually 0V
Digital circuits are usually easier to design however they can be expensive to build than an analog circuit that would do the same tasks