Table of Contents
| Dam used to hold back water |
What are Dams?
They are structured across a stream, river or anywhere where water needs to be retained.
They are usually constructed to provide water for human consumption, to help increasing the water to create hydroelectric energy and many more functions
Dam Components
Abutment
- The side of the valley at which the dam is constructed.
- An artificial abutment is sometimes created when there is no natural one present
Base Width
- It is the width that is measured along the foundation/dam interface
Top Width
- It is the the thickness or width of the dam at the top
Structural Height
- It is the vertical distance from the lowest point of natural ground on the downstream side of the dam to the highest part of the dam that would impound the water
Toe
- It is the junction of the downstream face of a dam with the natural ground surface.
Heel
- This is the junction of the upstream face of an arch dam with the foundation surface
Crest length
- The measured length from one abutment to another abutment
Emergency Action Plan
- It is a predetermined plan to prevent damage to the surrounding properties and the loss of lives if the dam were to break
Face
- It is the external surface of the dam that limits the structure
Flashboards
- The vertical distance between the water surface and the lowest elevation at which the water would flow over the dam, a section that is not designed to be overflowed
Foundation
- The natural material that the dam is placed on
Gate
- It is device where a leaf or a member is moved across the waterway from an external position to control or stop the flow
Spillway
- A structure over or through the dam at which flood flows are discharged
- If the flood is controlled by gates it is considered as a controlled spillway
- If the elevation of the spillway is the only control, it is considered as an uncontrolled spillway’
- Emergency spillway
- A secondary spillway that is meant to be used when exceptional flooding occurs
- Emergency spillway
Low level outlet
- It is an opening at the lower level of the reservoir. It is generally used to empty the impoundment
| Top Overview of the Dam |
| Plan/Horizontal View of the Dam | Section A-A as shown in Horizontal View |
| Plan/Vertical View of the Dam | Zoomed Shot of the Vertical View |
Video Explaining Conceptional Facts about Dams
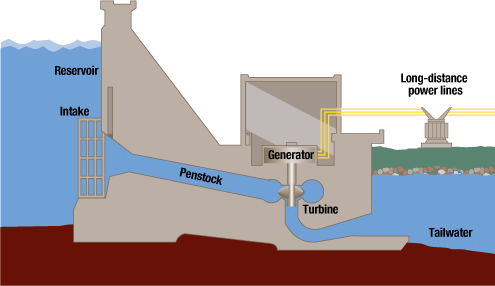
Dam Use Cases
Dams are used for Hydropower | Dams are also used to divert water |
Additional Readings
History of Dams & Dam Failures