Table of Contents
| Assorted Extruded Aluminum [1] |
What is Metal Extrusion?
Metal extrusion is the manufacturing process in which metal is forced through a die with a smaller cross-sectional area to produce an object with a fixed, shaped profile of variable length [2]. The resulting material called as extrusion may be formed with a unique profile allowing them to easily be used for prototyping items [3]. To connect the extrusions together, linear bearings, fasteners, and corner gussets are some components that can be used [3]. Commonly extruded metals include aluminum, copper, steel, magnesium, and lead; however, materials such as plastics, ceramics and concrete can also be extruded [2].
Manufacturing
Types of Extrusion
There are several types of extrusion classified by the process by which they are manufactured. These types include direct extrusion, indirect extrusion, hydrostatic extrusion, hot extrusion and cold extrusion.
Classification by flow of metal
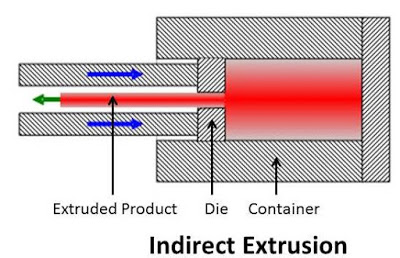
Direct extrusion is the process in which metal is forced to flow through the die in the direction of the movement of the ram. This process requires greater force due to the friction between the billet and the container [4]. | Indirect extrusion is the process in which metal is forced to flow through the die in the direction opposite to the movement of the plunger [4]. |
Hydrostatic Extrusion
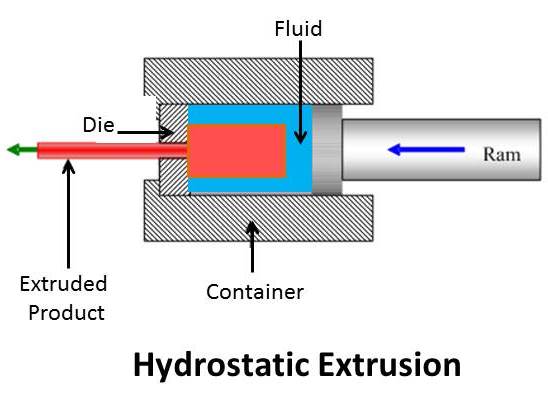
| Hydrostatic extrusion is a form of direct extrusion in which the extrusion piece is held in place by pressurized liquid (generally hydraulic oil). The ram applies a force upon the liquid which applies pressure to all surfaces of the work piece, forcing it though the die. This process eliminates friction, since the billet in neither in contact with the ram, nor container [4]. |
Hot Extrusion
If the extrusion occurs when the metal is above its recrystallization temperature, it is known as hot extrusion [4]. The recrystallization temperature of a metal is about 50-60% of its melting point [4]. Advantages to hot extrusion include a lower force required to extrude and easier manipulation. Additionally, hot working a metal improves its mechanical properties including impact resistance, ductility and strength. However, most metal extrusion is performed on billets that have already been hot formed thus have already gained the listed mechanical advantages [5]. Disadvantages to hot extrusion include a layer of resulting oxidation on the surface of the metal, increased die wear and maintenance of high working temperatures [5].
Cold Extrusion
Conversely, if the extrusion occurs when the metal is below its crystallization temperature, it is known as cold extrusion [4]. Metals such as aluminium which are easy to form are not required to be heated to be worked. Advantages to cold extrusion include not needing to heat the work, greater production rate, no oxidation on surfaces, and greater geometric accuracy [4].
Application
What is Metal Extrusion Used for?
Common applications of metal extrusion includes architecture and construction, display equipment, electrical systems, industrial and transportation. In construction, the extruded aluminium resists distortion as a result of weather and building movement thanks to its high flexibility under loads and its capability of springing back from shock of impact. One of its greatest attributes is that it is naturally resistant to rust and corrosion without additional treatment [6]. Aluminium extrusion is an efficient heat conductor, thus is often used in automobile radiators, air conditioners, condenser tubes, cooling devices in computers, nuclear reactors, etc [6]. In the transportation industry, aluminium extrusions are ideal for engine blocks, transmission housing, roof rails, car chassis, etc [6].
What are the Different Extrusion Profiles?
There are a number of extrusion profiles offered: box section, tube/hollow, T-slotted, and more. Of them, the T-slotted is the most popular and common. Typically, they are chosen based on the weight load. All the extrusions offer a weight load capacity. For designs using fasteners, an extrusion without a hollow middle would be preferable so the fastener is more attached to the extrusion.
T-Slot Aluminium Extrusion
T-slot aluminium extrusion is an excellent structural material which offers a wide variety of possibilities. It works well for structures such as machine frames, enclosures, safety guarding, etc. For further information about building with T-slotted extrusion, 80/20 Inc. has an excellent online guide: T-Slotted Aluminum: The Basics of Building [8].
| T-Slot Aluminium Extrusion Profiles [9] |
How to Connect Extrusions Together?
There are number of ways to connect aluminum extrusion pieces together. The modular design of the extrusion allows for many possible creations. Below are a few methods:
Fasteners
End fasteners are usually cheaper than anchor fasteners but require more work to install compared to an anchor fastener, as you need to screw a hole through the metal [10].
| End Fasteners [11] | Anchor Fasteners [10] |
Brackets, Gussets, and Plates
Corner gussets are triangular shaped and are slightly stronger than a corner bracket. All of these can be used for high load applications, although the preferred is the gusset or plates. They do not need machining. All come in fractional or metric and in a variety of sizes. Bolt assembly will be needed to install.
| Corner Bracket [12] | Corner Gusset [12] | Corner Plates [12] |
Additional Reading
Contributors:
| User | Last Update |
|---|---|
| Former user (Deleted) | 1317 days ago |
| Former user (Deleted) | 1317 days ago |
| Former user (Deleted) | 1328 days ago |
| Former user (Deleted) | 1362 days ago |