Former user (Deleted) Gigabit Ethernet is a transmission technology that is used to network devices in a wired local environment. This environment is called a Local Area Network (LAN) and allows connected devices to send and receive data over a cable at a rate of 1 billion bits per second. The main components include the RJ45 connector that connects to the ethernet cable, the 4 differential pairs that transmit data, and the controller that acts as a bridge between the ethernet and the PCIe or RGMII microcontrollers.
RJ45 Connector & Magnetics
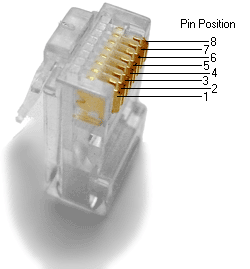
The RJ45 connector is the standard to connect to ethernet cable with 8 pins that correspond to 4 bi-directional differential pairs. In gigabit ethernet, all 4 differential pairs are used, and a minimum of Category 5 cable is required. Magnetic Transformers are required for these differential pairs to isolate the communication wires from the rest of the system and ensure that their signal isn’t corrupted by any faults elsewhere. They can either be integrated in the RJ45 connector, or added externally in the schematic design.
Resources:
https://www.avnet.com/wps/portal/abacus/resources/article/ethernet-magnetics-discrete-or-integrated/
4 Transmit and Receive Differential Pairs
Gigabit ethernet uses 4 differential pairs to transmit and receive data. Each of these pairs are bi-directional, and therefore backwards compatible with slower methods of ethernet. The naming and colour codes for these pairs are seen below:
Differential pair A is set to tranceive, and pair B is set to receive data.
Resources:
http://www.interfacebus.com/Gigabit_Ethernet_Description.html
https://allpinouts.org/pinouts/connectors/networking/ethernet-1000base-t-gigabit/
Controller
- bridging between ethernet and PCIE/RGMII
- Reference Clock
- EEPROM storage
.png?version=1&modificationDate=1617407629297&cacheVersion=1&api=v2&height=250)